Note
Click here to download the full example code
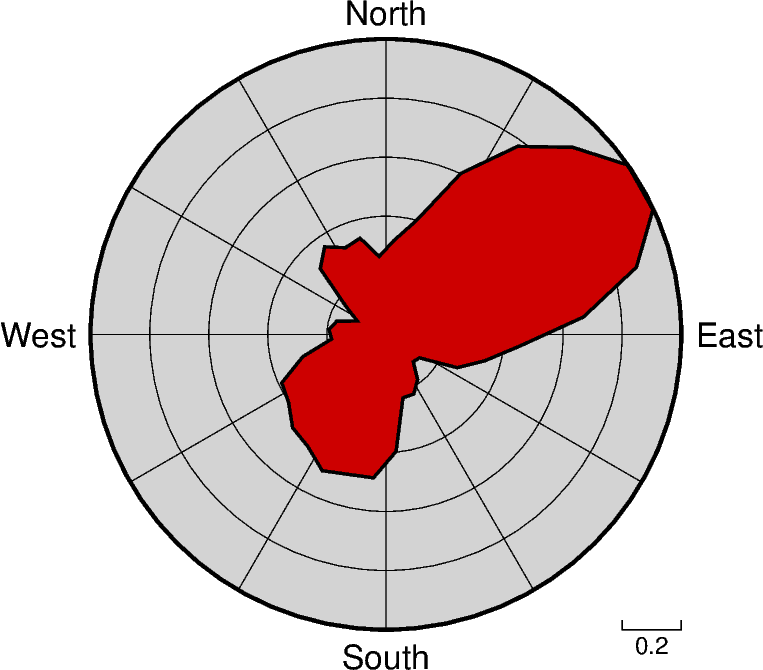
Rose diagram
The pygmt.Figure.rose method can plot windrose diagrams or polar
histograms.
Out:
/vercel/path0/pygmt/helpers/decorators.py:809: FutureWarning: The function parameters has been re-ordered as 'data, x, y, [z]' since v0.5.0 but you're passing positional arguments. You can silence the warning by passing keyword arguments like 'x=x, y=y, z=z'. Otherwise, the warning will be removed in v0.7.0.
return module_func(*args, **kwargs)
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
import pygmt
# Load sample compilation of fracture lengths and azimuth as
# hypothetically digitized from geological maps
data = pygmt.datasets.load_fractures_compilation()
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.rose(
# use columns of the sample dataset as input for the length and azimuth
# parameters
length=data.length,
azimuth=data.azimuth,
# specify the "region" of interest in the (r,azimuth) space
# [r0, r1, az0, az1], here, r0 is 0 and r1 is 1, for azimuth, az0 is 0 and
# az1 is 360 which means we plot a full circle between 0 and 360 degrees
region=[0, 1, 0, 360],
# set the diameter of the rose diagram to 7.5 cm
diameter="7.5c",
# define the sector width in degrees, we append +r here to draw a rose
# diagram instead of a sector diagram
sector="10+r",
# normalize bin counts by the largest value so all bin counts range from
# 0 to 1
norm=True,
# use red3 as color fill for the sectors
color="red3",
# define the frame with ticks and gridlines every 0.2
# length unit in radial direction and every 30 degrees
# in azimuthal direction, set background color to
# lightgray
frame=["x0.2g0.2", "y30g30", "+glightgray"],
# use a pen size of 1p to draw the outlines
pen="1p",
)
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.505 seconds)